

|
Документ взят из кэша поисковой машины. Адрес
оригинального документа
: http://www.stsci.edu/~inr/thisweek1/2009/thisweek103.html
Дата изменения: Mon Apr 13 23:49:23 2009 Дата индексирования: Tue Aug 18 11:52:20 2009 Кодировка: Поисковые слова: http astrokuban.info astrokuban |


| Program Number | Principal Investigator | Program Title | Links |
| 11113 | Keith S. Noll, Space Telescope Science Institute | Binaries in the Kuiper Belt: Probes of Solar System Formation and Evolution | Abstract |
| 11212 | Douglas R. Gies, Georgia State University Research Foundation | Filling the Period Gap for Massive Binaries | Abstract |
| 11298 | John P. Subasavage, Georgia State University Research | Calibrating Cosmological Chronometers: White Dwarf Masses | Abstract |
| 11603 | Jennifer Andrews, Louisiana State University and A & M College | A Comprehensive Study of Dust Formation in Type II Supernovae with HST, Spitzer and Gemini | Abstract |
| 11943 | Douglas R. Gies, Georgia State University Research Foundation | Binaries at the Extremes of the H-R Diagram | Abstract |
| 11944 | Douglas R. Gies, Georgia State University Research Foundation | Binaries at the Extremes of the H-R Diagram | Abstract |
| 11974 | Sahar S. Allam, Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory | High-resolution imaging for 9 very bright, spectroscopically confirmed, group-scale lenses | Abstract |
| 11975 | Francesco R. Ferraro, Universita de Bologna | UV light from old stellar populations: a census of UV sources in Galactic Globular Clusters | Abstract |
| 11977 | Nathan Smith, University of California - Berkeley | WFPC2 12-Year Proper Motions of Two Galactic Analogs of the SN1987A Rings | Abstract |
| 11978 | Tommaso L. Treu, University of California - Santa Barbara | Luminous and dark matter in disk galaxies from strong lensing and stellar kinematics | Abstract |
| 11980 | Sylvain Veilleux, University of Maryland | Deep FUV Imaging of Cooling Flow Clusters | Abstract |
| 11981 | Jesus Maiz Apellaniz, Instituto de Astrofisica de Andalucia | FUV imaging survey of Galactic open clusters | Abstract |
| 11982 | Scott F. Anderson, University of Washington | Spanning the Reionization History of IGM Helium: a Large and Efficient HST Spectral Survey of Far-UV-Bright Quasars | Abstract |
GO 11113: Binaries in the Kuiper Belt: Probes of Solar System Formation and Evolution
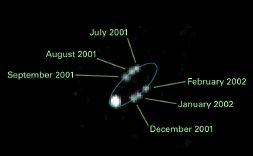 A composite of HST images of the Kuiper Belt binary, WW31
A composite of HST images of the Kuiper Belt binary, WW31
|
The Kuiper Belt consists of icy planetoids that orbit the Sun within a broad band stretching from Neptune's orbit (~30 AU) to distance sof ~50 AU from the Sun (see David Jewitt's Kuiper Belt page for details). Over 500 KBOs are currently known out of a population of perhaps 70,000 objects with diameters exceeding 100 km. Approximately 2% of the known KBOs are binary (including Pluto, one of the largest known KBOs, regardless of whether one considers it a planet or not). This is a surprisingly high fraction, given the difficulties involved in forming such systems and the relative ease with which they can be disrupted. It remains unclear whether these systems formed from single KBOs (through collisions or 3-body interactions) as the Kuiper Belt and the Solar System have evolved, or whether they represent the final tail of an initial (much larger) population of primordial binaries. This proposal will use WFPC2 imaging of known KBOs to identify new binary systems. |
GO 11298: Calibrating Cosmological Chronometers: White Dwarf Masses
GO 11977: WFPC2 12-Year Proper Motions of Two Galactic Analogs of the SN1987A Rings
GO 11982: Spanning the Reionization History of IGM Helium: a Large and Efficient HST Spectral Survey of Far-UV-Bright Quasars
 GALEX image of the nearby spiral, M81
GALEX image of the nearby spiral, M81
|
The reionisation epoch for intergalactic helium is thought to occur somewhere between redshifts 3 and 4. Observations with the GALEX satellite, a NASA small explorer-class mission equipped with a 50-cm diameter telescope, are proving critical in testing this hypothesis through the identification of UV bright quasars in the appropriate redshift range. Galex was launched on 28th April 2003, and continues to operate more than 30 months beyond its nominal lifetime, conducting ultraviolet imaging and low-resolution grism spectroscopy at far-UV (125-175 nm) and near-UV (175-280 nm) wavelengths. Past HST programs by this research have used the ACS/SBC to target sources identified by cross-referencing GALEX against SDSS catalogues of moderate (1 < z < 3) and high redshift (z > 3.1) quasars. These sources can serve as effective probes of the ionisation state of the intergalactic medium at intervening redshifts. In particular, analysis of the He II Lyman-alpha absorption will shed light on the epoch of reionisation of intergalactic helium, generall placed between redshifts 3 and 4. The present program will use the ACS/SBC PR120L prism for spectroscopy of 40 QSOs with redshifts in the range 3.1 < z < 5.1. |