|
(Обзор литературы)
В.С. Горин, В.Н. Серов, С.Г. Жабин, О.Б. Дубленников, А.Г. Маркдорф, Р.В. Горин
Институт усовершенствования врачей, Новокузнецк; Научный центр акушерства, гинекологии и перинатологии, Москва; Центр охраны здоровья матери и ребенка, Новокузнецк
Проблемы репродукции, 3-1999, с.22-28
В начало...
(Окончание)
1. Wald N.J., Cuckle H.S., Densern J.W. et al. Maternal serum screening for Down's syndrome in early pregnancy. Br Med J 1988; 297: 883-887.
2. Brambati В., Lanzani A., Tului L. Ultrasound and biochemical assessment of first trimester pregnancy. In: Chapman M. Grudzinskas G. and Chard T. ed. The embryo: normal and abnormal development and growth. New York: Springer-Verlag. 1991; 181-194.
3. Spencer K., Maсri J.N., Aitken D.A., Connor J.M. Free 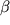 -hCG as first trimester marker for fetal trisomy. Lancet 1992; 339: 1480. -hCG as first trimester marker for fetal trisomy. Lancet 1992; 339: 1480.
4. Brambati В., Tului L., Bonacchi I. et al. Serum PAPP-A and free 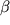 -hCG are first trimester screening markers for Down'ssyndrome. Hum Reprod 1993; 8 (suppl. 1): 183. -hCG are first trimester screening markers for Down'ssyndrome. Hum Reprod 1993; 8 (suppl. 1): 183.
5. Bischof P. Purification and characterization of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A). Arch Gynecol 1979; 227: 315-326.
6. Sinosich M.J. Molecular characterization of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A by electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 1990; 11: 70-78.
7. Зорин Н.А., Жабин С.Г., Белогорлова Т.И., Архипова С.В. Сравнительное изучение 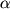 2-макроглобулина и ассоциированных с беременностью 2-макроглобулина и ассоциированных с беременностью 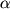 2-гликопротеина и протеина А как возможных аналогов. Вопр Мед Хим; 1993; 3: 48-50. 2-гликопротеина и протеина А как возможных аналогов. Вопр Мед Хим; 1993; 3: 48-50.
8. Oxvig С., Sand O., Kristensen T. et al. Circulating human pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A is disulfide-bridged to the proform of eosinophil major basic protein. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 12243-12246.
9. Исследование системы крови в клинической практике. Под ред. Г.И. Козинца и В.А. Макарова. М 1997; 480.
10. Kristensen Т., Oxvig С., Sand О. et al. Amino acid sequence of human pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A derived from cloned cDNA. Biochemistry 1994; 33: 1572-1598.
11. Bersinger N.A., Brizot M.L. Lectin binding of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A purified from different sources. Biochem Soc Trans 1996; 24: 498.
12. Sutcliffe R.G., Kukulska-Langlands B.M., Coggins J. et al. Studies on human pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A. Purification by affinity chromatography and structural comparisons with 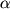 2-macroglobulin. Biochem J 1980; 191: 799-809. 2-macroglobulin. Biochem J 1980; 191: 799-809.
13. Zorin N.A., Zhabin S.G., Semenkov N.N. Interaction of human pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A with serineproteinases. Clin Chem Acta 1995; 239: 47-55.
14. Sinosich M.J., Davey M.W., Ghosh P., Grudzinskas J.G. Specific inhibition of human granulocyte elastase by human pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A. Biochem Int 1982; 5: 777-786.
15. Мальцева Н.В., Горин B.C., Жабин С.Г., Зорин Н.А. Сравнительное изучение иммуносупрессорных свойств ассоциированного с беременностью протеина А и 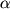 2-гликопротеина, а также 2-гликопротеина, а также 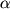 2-макроглобулина. Акуш гинекол 1991; 5: 27-30. 2-макроглобулина. Акуш гинекол 1991; 5: 27-30.
16. Мусатов М.И., Жабин С.Г., Протопопов Б.В. и др. Влияние ассоциированного с беременностью протеина А на первичную аллогенную смешанную культуру лимфоцитов человека. Иммунология 1992; 3: 59-60.
17. Зорин Н.А., Зорина P.M., Горин B.C. и др. Семейство макроглобулинов (обзор литературы). Клин лаб диагн 1993; 1: 52-56.
18. El Farra К., Grudzinskas J.G. Will PAPP-A be a biochemical marker for screening of Down's syndrome in the first trimester? Early Pregnancy 1995; 1: 4-12.
19. Bersinger N.A., Alternatt H.J. Brikh дuser M.H. et al. Non-placental production of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A): old and new evidence. Early Pregnancy 1997; 3: 96-101.
20. Schindler A.M., Dayer A., Bischof P. Immunohistochemical localization of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A in the male genital tract. Hum Reprod 1986; 1: 55-59.
21. Bischof P., Sizonenko M.T. Herrmann W.L. Trophoblastic and decidual response to RU486: effects on human chorionic gonadotrophin, human placental lactogen, prolactin and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A production in vitro. Hum Reprod 1986; 1: 3-6.
22. Bonno M., Oxvig C., Kephart G.M. et al. Localization of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A and colocalization of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A messenger ribonucleic acid and eosinophil granule major basic protein messnger ribonucleic acid in placenta. Lab Invest 1994; 71: 560-566. 23. Sabet L.M., Daya D., Stead R. et al. Significance and value of immunohistochemical localization of pregnancy specific proteins in fetomaternal tissue throughout pregnancy. Mod Pathol 1989; 2: 227-232.
24. Chemnitz J., Folkersen J., Teisner B. et al. Comparison of different antibody preparations against pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) for use location and immunoassay studies. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1986; 93: 916-923.
25. Bersinger N.A., Brandenberger A.W., Birkhuser M.H. Endometrial and placental protein markers and ovarian steroids in serum during in vitro fertilization cycles. Hum Reprod 1995; 10: 2149-2154.
26. Sorensen S., Momsen G., Ruge S., Pedersen J.F. Differential increase in the maternal serum conxentrations of the placental proteins human chorionic gonadotrophin, pregnancy-specific 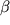 1-glycoprotein, human placental lactogen and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A during the first half of normal pregnancy elucidated by means of a mathematical model. Hum Reprod 1995; 10: 453-458. 1-glycoprotein, human placental lactogen and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A during the first half of normal pregnancy elucidated by means of a mathematical model. Hum Reprod 1995; 10: 453-458.
27. Зорин Н.А., Горин B.C., Зорина P.M. и др. Белки беременности у небеременных, беременных, рожениц и родильниц. Акуш и гин 1990; 3: 65-67.
28. Жабин С.Г., Зорин Н.А., Мальцева Н.В. Иммуноферментный метод определения концентрации ассоциированного с беременностью протеина-А. Лаб Дело 1989; 12: 52- 54.
29. Knight G.J., Palomaki G.E., Haddow J.E. et al. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A as a marker for Down's syndrome in the second trimester of pregnancy (letter). Prenat Diag 1993; 13: 222-223.
30. Qin Qin-Ping, Christiansen M., Oxvig C. et al. Double-monoclonal immunofluorometric assay for pregnancy-associated plasma protein A / proeosinophil major basic protein (PAPP-A/proMBP) complex in first-trimester maternal serum screening for Down syndrome. Clin Chem 1997; 43: 2323-2332. 31. Qin Qin-Ping, Christiansen M. Lovgren T. et al. Duallabel time-resolved immunofluorometric assay for simultaneous determination of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A and free beta-subunit of human chorionic gonadotrophin. J Immunol Meth 1997; 205: 169-175.
32. Pedersen J.F., Sorensen S., Molsted Pedersen L. Serum levels of human placental lactogen, pregnancy-associated plasma protein A and endometrial secretory protein PP14 in first trimester of diabetic pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1998; 77: 155-158.
33. Bersinger N.A., Marguerat P., Pescia G., Schneider H. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A): measurement by highly sensitive and specific enzyme immunoassay, importance of first-trimester serum determinations, and stability studies. Reprod Fertil Dev 1995; 7: 1419-1423.
34. Haddow J.E., Palomaki G.E., Knight G.J. et al. Screening of maternal serum for fetal Down's syndrome in the first trimester. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 955-961.
35. Berry E., Aitken D.A. Crossley J.A. et al. Screening for Down's syndrome: changes in marker levels and detection rates between first and second trimesters. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1997; 104: 811-817.
36. Wald N.J., Hackshaw A.K. Combining ultrasound and biochemistry in first-trimester screening for Down's syndrome. Prenat Diag 1997; 17: 821-829.
37. Krantz D.A., Larsen J.W., Buchanan P.D., Macri J.N. First-trimester Down syndrome screening: free beta-human chorionic gonadotrophin and pregnancy-associated plasma protein A. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996; 174: 612-616.
38. Aitken D.A., McKinnon D., Crossley J.A. et al. Changes in the in Down's maternal serum concentrations of PAPP-A and SP1 syndrome pregnancies between the first and second trimester. J Med Genet 1994; 31: 170-178.
39. Casals E., Fortuna A., Grudzinskas J.G. et al. First-trimester biochemical screening for Down syndrome with the use of PAPP-A, AFP, and 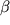 -hCG. Prenat Diag 1996; 16: 405-410. -hCG. Prenat Diag 1996; 16: 405-410. 40. Bersinger N.A., Brizot M.L., Johnson A. et al. First trimester maternal serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein A and pregnancy-specific 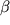 1-glycoprotein in fetal trisomies. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1994; 101: 970-974. 1-glycoprotein in fetal trisomies. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1994; 101: 970-974.
41. Macintosh M.C., Brambati В., Chard Т., Grudzinskas J.G. Predicting fetal chromosome anomalies in the first trimester using pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A: a comparison of statistical methods. Methods Inf Med 1993; 32: 175-179. 42. Brizot M.L., Snijders R.J., Bersinger N.A. et al. Maternal serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein A and fetal nuchal translucency thickness for the prediction of fetal trisomies in early pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1994; 84: 918-922.
43. Westergaard J.G., Teisner B., Poulsen H.K. et al. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A: a possible marker in the classification and prenatal diagnosis of Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Prenat Diag 1983; 3: 225-232.
44. Wheeler D.M., Edirisinghe W.R., Petchell F. et al. Trophoblast antigen levels in the first trimester of a trisomy 22 pregnancy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1996; 66: 197-199. 45. Wenstrom K.D., Owen J., Chu D.C., Boots L. Elevated second-trimester dimeric inhibition A levels identify Down syndrome pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997; 177: 992-996.
46. Wenstrom K.D., Owen J., Chu D.C., Boots L. 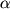 -Fetoprotein, free -Fetoprotein, free 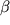 -human chorionic gonadotrophin, and dimeric inhibinA produce the best results in a three-analyte, multiple-marker screening test for fetal Down syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997; 177: 987-991. -human chorionic gonadotrophin, and dimeric inhibinA produce the best results in a three-analyte, multiple-marker screening test for fetal Down syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997; 177: 987-991.
47. Stabile I., Campbell S., Grudzinskas J.G. Treatened miscarriage and intrauterine hematomas sonographic and biochemical studies. J Ultrasound Med 1985; 8: 289-292.
48. Pedersen J.P., Ruge S., Serensen S. Serum levels of hPL (placental lactogen), PAPP-A and PP14 in patients with early pregnancy bleeding and subchorionic hemorrhage. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1995; 74: 30-32.
49. Morssink L.P., Kornman L.H., Hallahan T.W. et al. Maternal serum levels of free beta-hCG and PAPP-A in the first trimester of pregnancy are not associated with subsequent fetal growth retardation or preterm delivery. Prenat Diag 1998; 18: 147-152.
50. Johnson M.R., Riddle A.F., Grudzinskas J.G. et al. Reduced circulating placental protein concentrations during the first trimester are associated with preterm labour and low birth weight.
Hum Reprod 1993; 8: 1942-1947.
51. Westergaard J.G., Sinosich M.J., Bugge M. et al. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein A in the prediction of early pregnancy failure. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983; 145: 67-69. 52. Bersinger N.A., Keller P.J., Naiem A. et al. Pregnancy-specific and pregnancy-associated proteins in threatened abortion.
Gynecol Endocrinol 1987; 1: 379-384.
53. Poulsen H.K., Westergaard J.G., Teisner B., Bolton A.E., Norman R.G., Grudzinskas J.G. Measurements of hCG and PAPP-A in uncommon types of ectopic gestation. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1987; 26: 33-37.
54. Sinosich M.J., Torode H., Saunders D. Diagnosis and management of extrauterine pregnancies. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 1993; 33: 307-311.
55. Johnson M.R., Bolton V.N., Riddle A.F. et al. Interactions between the embryo and corpus luteum. Hum Reprod 1993; 8: 1496-1501.
56. Abbas A., Sebire N.J., Johnson M. et al. Maternal serum concentrations of pregnancy-associated placental protein A and pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein in multifetal pregnancies before and fetal reduction. Hum Reprod 1996; 11: 900- 902.
57. Жабин С.Г., Дубленников О.Б., Краюшкина Н.А. Белки беременности при аномалиях и внутриутробной задержке развития плода у женщин с первично низким расположением плаценты. В кн. <Прогнозирование и профилактика нарушений здоровья матери и ребенка>. М 1988; 126-129. 58. Pedersen J.F., Sorensen S., Molsted Pedersen L. Serum levels of human placental lactogen, pregnancy-associated plasma protein A and endometrial secretory protein PP14 in first trimester of diabetic pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1998; 77: 155-158.
59. Sutcliffe R.G., Kukulska-Langlands B.M., Coggins J. et al. Studies of the concentrations of human pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A during normal and complicated pregnancy. Placenta 1982; 3: 71-80.
60. Brizot M.L., Jauniaux E., McKie A.T. et al. Placental expression of 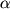 and and 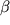 subunits of human chorionic gonadotrophin in early pregnancy with Down's syndrome. Hum Reprod 1995; 10: 2506-2509. subunits of human chorionic gonadotrophin in early pregnancy with Down's syndrome. Hum Reprod 1995; 10: 2506-2509.
61. Brizot M.L., Hyett A., McKie A.T. et al. Gene expression of human pregnancy-associated plasma protein A in placenta from trisomic pregnancies. Placenta 1996; 17: 33-36.
Написать комментарий
| 
