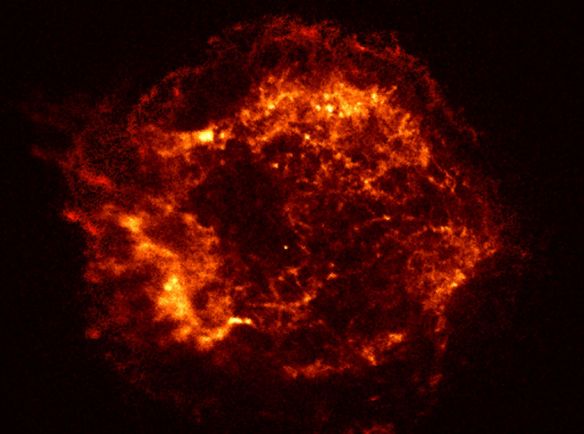
Chandras First Light: Cassiopeia A
Explanation:
Cosmic wreckage from the detonation of a massive star is the
subject of
this official first image from NASA's
Chandra X-ray Observatory.
The supernova remnant, known as
Cassiopeia A, was produced when
a star exploded around 300 years ago in
this northern sky constellation.
It is revealed here in unprecedented
detail in the
light of X-rays - photons with thousands of times the energy
of visible light.
Shock waves expanding at 10 million miles-per-hour
are seen to have heated this 10 light-year diameter
bubble of stellar debris
to X-ray emitting temperatures of 50 million
kelvins.
The tantalizing bright speck near the bubble's center could
well be the dense, hot remnant of the stellar core collapsed to form a
newborn neutron star.
With this and other
first light images, the Chandra
Observatory is still undergoing check out operations in preparation
for its much anticipated exploration of the X-ray sky.
Chandra was launched
aboard the space shuttle Columbia in July.
Authors & editors:
Robert Nemiroff
(MTU) &
Jerry Bonnell
(USRA)
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings,
and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris.
Specific
rights apply.
A service of:
LHEA at
NASA /
GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.