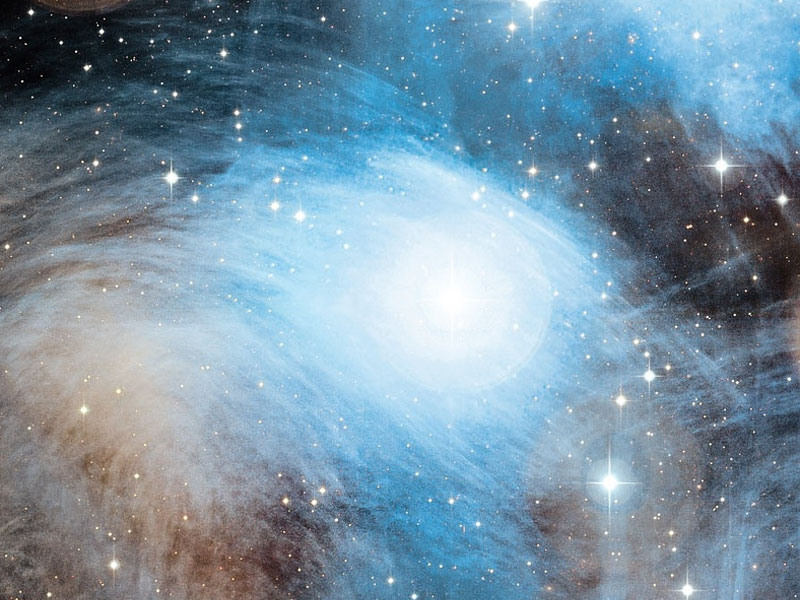
The Merope Reflection Nebula

Explanation:
Reflection nebulas reflect light from a nearby star.
Many small
carbon
grains in the nebula reflect the light.
The blue color typical of
reflection nebula is caused by blue light being
more efficiently scattered by the carbon
dust than red light.
The brightness of the nebula is determined by the
size and density of the reflecting grains,
and by the color and brightness of the neighboring star(s).
NGC 1435,
pictured above, surrounds
Merope (23 Tau), one of the brightest stars in the
Pleiades (M45).
The
Pleiades nebulosity is caused by a
chance encounter between an
open cluster of stars and a
molecular cloud.
Authors & editors:
Robert Nemiroff
(MTU) &
Jerry Bonnell
(USRA)
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings,
and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris.
Specific
rights apply.
A service of:
LHEA at
NASA /
GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.