|
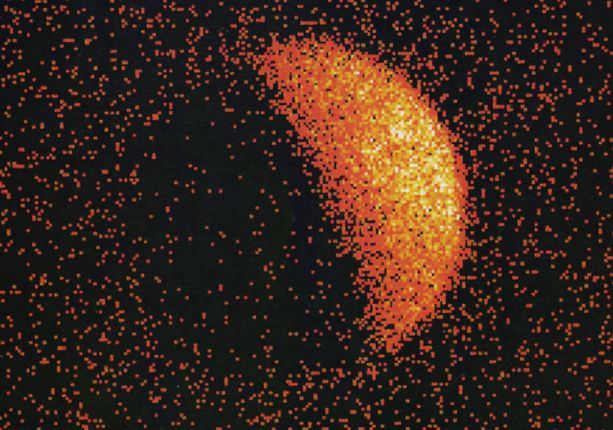
Explanation: This x-ray image of the Moon was made by the orbiting ROSAT (Röntgensatellit) Observatory in 1990. In this digital picture, pixel brightness corresponds to x-ray intensity. Consider the image in three parts: the bright hemisphere of the x-ray moon, the darker half of the moon, and the x-ray sky background. The bright lunar hemisphere shines in x-rays because it scatters x-rays emitted by the sun. The background sky has an x-ray glow in part due to the myriad of distant, powerful active galaxies, unresolved in the ROSAT picture but recently detected in Chandra Observatory x-ray images. But why isn't the dark half of the moon completely dark? It's true that the dark lunar face is in shadow and so is shielded from direct solar x-rays. Still, the few x-ray photons which seem to come from the moon's dark half are currently thought to be caused by energetic particles in the solar wind bombarding the lunar surface.
Tomorrow's picture: Night Sky Live
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Based on Astronomy Picture
Of the Day
Publications with keywords: Moon - cosmic rays - x-ray background
Publications with words: Moon - cosmic rays - x-ray background
See also: