
|
Keyword: gamma-ray burst
 Cyg X-1: Can Black Holes Form in the Dark?
Cyg X-1: Can Black Holes Form in the Dark?
2.04.2005
The formation of a black hole from the collapsing core of a massive star is thought to be heralded by a spectacular supernova explosion. Such an extremely energetic collapse is also a leading explanation for the mysterious cosmic gamma-ray bursts.
 ESO 184 G82: and the Supernova Gamma Ray Burst Connection
ESO 184 G82: and the Supernova Gamma Ray Burst Connection
28.02.2002
Modern astronomers keep a long list of things that go bump in the night. Near the top are supernovae - the death explosions of massive stars, and gamma-ray bursts - the most powerful explosions seen across the Universe.
 Cyg X-1: Can Black Holes Form in the Dark
Cyg X-1: Can Black Holes Form in the Dark
12.06.2003
The formation of a black hole from the collapsing core of a massive star is thought to be heralded by a spectacular supernova explosion. Such an extremely energetic collapse is also a leading explanation for the mysterious cosmic gamma-ray bursts.
 Gamma Ray Burst Afterglow: Supernova Connection
Gamma Ray Burst Afterglow: Supernova Connection
5.04.2002
What causes the mysterious gamma-ray bursts? Indicated in this Hubble Space Telescope exposure of an otherwise unremarkable field in the constellation Crater, is the dwindling optical afterglow of a gamma-ray burst first detected by the Beppo-SAX satellite on 2001 December 11.
 A GRB 000301C Symphony
A GRB 000301C Symphony
14.03.2000
Telescopic instruments in Earth and space are still tracking a tremendous explosion that occurred across the universe. A nearly unprecedented symphony of international observations began abruptly on March 1 when Earth-orbiting RXTE, Sun-orbiting Ulysses, and asteroid-orbiting NEAR all detected a 10-second burst of high-frequency gamma radiation.
 Supernova Factory NGC 2770
Supernova Factory NGC 2770
18.01.2008
The stellar explosions known as supernovae are among the most powerful events in the universe. Triggered by the collapsing core of a massive star or the nuclear demise of a white dwarf, supernovae occur in average spiral galaxies only about once every century.
 Across the Universe
Across the Universe
28.03.2008
How far can you see? Even the faintest stars visible to the eye are merely hundreds or thousands of light-years distant, all well within our own Milky Way Galaxy. Of course, if you know where to look you can also spot the Andromeda Galaxy as a pale, fuzzy cloud, around 2.5 million light-years away.
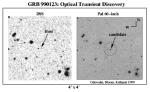 Galaxy And Gamma Ray Burst
Galaxy And Gamma Ray Burst
25.01.1999
Gamma-ray bursts rule the high-energy sky and Saturday another brief, intense flash of gamma-rays from the cosmos triggered space-based detectors. The orbiting Compton Observatory's BATSE instrument quickly relayed the burst's approximate location to fast-slewing, ground-based cameras primed to search for an elusive optical flash.
 GRB 990510: Another Unusual Gamma Ray Burst
GRB 990510: Another Unusual Gamma Ray Burst
26.05.1999
Another huge explosion has lit up the universe, and astronomers are studying it as best they can before the light fades away. Two weeks ago, the BATSE instrument on the orbiting NASA Great Observatory Compton detected unusually bright flashes of gamma-rays from a point deep in the southern sky.
 GRB 060218: A Mysterious Transient
GRB 060218: A Mysterious Transient
27.02.2006
What is it? Something is happening in a small portion of the sky toward the constellation of Aries and telescopes around the globe are tracking an unusual transient there as it changes day by day. No one is sure what it will do next.
|
January February |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||