
|
Keyword: supernova remnant
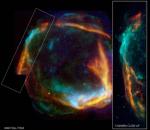 APOD: 2006 September 28- RCW 86: Historical Supernova Remnant
APOD: 2006 September 28- RCW 86: Historical Supernova Remnant
28.09.2006
In 185 AD, Chinese astronomers recorded the appearance of a new star in the Nanmen asterism - a part of the sky identified with Alpha and Beta Centauri on modern star charts. The new star was visible for months and is thought to be the earliest recorded supernova.
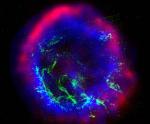 Supernova Remnant E0102 72 from Radio to X-Ray
Supernova Remnant E0102 72 from Radio to X-Ray
14.04.2000
Not all stars form a big Q after they explode. The shape of supernova remnant E0102-72, however, is giving astronomers a clue about how tremendous explosions disperse elements and interact with surrounded gas. The above image is a composite of three different photographs in three different types of light.
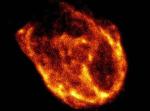 Supernova Remnant N132D in X Rays
Supernova Remnant N132D in X Rays
13.09.1999
Thousands of years after a star explodes, an expanding remnant may still glow brightly. Such is the case with N132D, a supernova remnant located in the neighboring Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy. The expanding shell from this explosion now spans 80 light-years and has swept up about 600 Suns worth of mass.
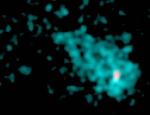 IC443's Neutron Star
IC443's Neutron Star
14.12.2000
Using x-ray data from the orbiting Chandra Observatory along with radio data from the Very Large Array, a team of researchers has discovered evidence for a new example of one of the most bizarre objects known to modern astrophysics -- a neutron star.
 N49 s Cosmic Blast
N49 s Cosmic Blast
4.07.2003
Scattered debris from a cosmic supernova explosion lights up the sky in this gorgeous composited image based on data from the Hubble Space Telescope. Cataloged as N49, these glowing filaments of shocked gas span about 30 light-years in our neighboring galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud.
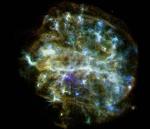 Elements in the Aftermath
Elements in the Aftermath
26.10.2001
Massive stars spend their brief lives furiously burning nuclear fuel. Through fusion at extreme temperatures and densities surrounding the stellar core, nuclei of light elements like Hydrogen and Helium are combined to heavier elements like Carbon, Oxygen, etc. in a progression which ends with Iron.
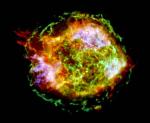 APOD: 2004 August 26- Cassiopeia A in a Million
APOD: 2004 August 26- Cassiopeia A in a Million
26.08.2004
One million seconds of x-ray image data were used to construct this view of supernova remnant Cassiopeia A, the expanding debris cloud from a stellar explosion. The stunningly detailed image from the Chandra Observatory will allow an unprecedented exploration of the catastrophic fate that awaits stars much more massive than the Sun.
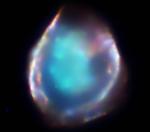 DEM L71: When Small Stars Explode
DEM L71: When Small Stars Explode
13.03.2003
Large, massive stars end their furious lives in spectacular supernova explosions -- but small, low mass stars may encounter a similar fate. In fact, instead of simply cooling off and quietly fading away, some white...
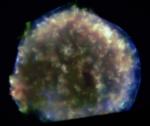 X Rays From Tycho s Supernova Remnant
X Rays From Tycho s Supernova Remnant
22.05.2004
In 1572, Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe recorded the sudden appearance of a bright new star in the constellation Cassiopeia. The new star faded from view over a period of months and is believed to have been a supernova, one of the last stellar explosions seen in our Milky Way galaxy.
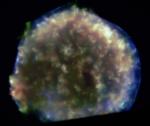 X Rays From Tycho s Supernova Remnant
X Rays From Tycho s Supernova Remnant
12.09.2002
In 1572, Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe recorded the sudden appearance of a bright new star in the constellation Cassiopeia. The new star faded from view over a period of months and is believed to have been a supernova, one of the last stellar explosions seen in our Milky Way galaxy.
|
January February |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||