
|
You entered: Cygnus
 Flemings Triangular Wisp
Flemings Triangular Wisp
27.07.2021
Chaotic in appearance, these tangled filaments of shocked, glowing gas are spread across planet Earth's sky toward the constellation of Cygnus as part of the Veil Nebula. The Veil Nebula itself is a large supernova remnant, an expanding cloud born of the death explosion of a massive star.
 Pickerings Triangle from Kitt Peak
Pickerings Triangle from Kitt Peak
1.07.2008
Wisps like this are all that remain visible of a Milky Way star. About 7,500 years ago that star exploded in a supernova leaving the Veil Nebula, also known as the Cygnus Loop.
 APOD: 2023 November 21 Б Flemings Triangular Wisp
APOD: 2023 November 21 Б Flemings Triangular Wisp
21.11.2023
These chaotic and tangled filaments of shocked, glowing gas are spread across planet Earth's sky toward the constellation of Cygnus as part of the Veil Nebula. The Veil Nebula itself is a large supernova remnant, an expanding cloud born of the death explosion of a massive star.
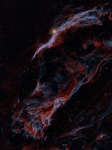 Along the Western Veil
Along the Western Veil
19.09.2019
Delicate in appearance, these filaments of shocked, glowing gas, are draped across planet Earth's sky toward the constellation of Cygnus. They form the western part of the Veil Nebula. The Veil Nebula itself is a large supernova remnant, an expanding cloud born of the death explosion of a massive star.
 Pickering s Triangle in the Veil
Pickering s Triangle in the Veil
17.09.2015
Chaotic in appearance, these filaments of shocked, glowing gas break across planet Earth's sky toward the constellation of Cygnus, as part of the Veil Nebula. The Veil Nebula itself is a large supernova remnant, an expanding cloud born of the death explosion of a massive star.
 Williamina Fleming s Triangular Wisp
Williamina Fleming s Triangular Wisp
10.11.2017
Chaotic in appearance, these tangled filaments of shocked, glowing gas are spread across planet Earth's sky toward the constellation of Cygnus as part of the Veil Nebula. The Veil Nebula itself is a large supernova remnant, an expanding cloud born of the death explosion of a massive star.
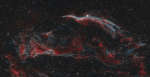 Along the Western Veil
Along the Western Veil
6.09.2018
Delicate in appearance, these filaments of shocked, glowing gas, are draped across planet Earth's sky toward the constellation of Cygnus. They form the western part of the Veil Nebula. The Veil Nebula itself is a large supernova remnant, an expanding cloud born of the death explosion of a massive star.
 Along the Western Veil
Along the Western Veil
4.04.2014
Delicate in appearance, these filaments of shocked, glowing gas, draped in planet Earth's sky toward the constellation of Cygnus, make up the western part of the Veil Nebula. The Veil Nebula itself is a large supernova remnant, an expanding cloud born of the death explosion of a massive star.
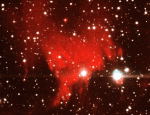 Nebula Nova Cygni Turns On
Nebula Nova Cygni Turns On
16.12.1996
Old photographs show no evidence of the above nebula. In 1992, a white dwarf star in Cygnus blew off its outer layers in a classical nova explosion: an event called Nova Cygni 1992. Light flooded the local interstellar neighborhood, illuminated this existing gas cloud, excited the existing hydrogen, and hence caused the red emission.
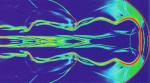 Jet Near Light Speed
Jet Near Light Speed
24.11.1997
Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity says that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light. Jets of protons and electrons that shoot away from objects such as quasars and black holes appear to travel at speeds approaching this maximum speed, though. Such jets carry tremendous energy and can ram straight through interstellar material.
|
January February |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||