
|
You entered: magellanic clouds
 The Mysterious Rings of Supernova 1987A
The Mysterious Rings of Supernova 1987A
5.03.2017
What's causing those odd rings in supernova 1987A? Thirty years ago, in 1987, the brightest supernova in recent history was seen in the Large Magellanic Cloud. At the center of the featured picture is an object central to the remains of the violent stellar explosion.
 R136: The Massive Stars of 30 Doradus
R136: The Massive Stars of 30 Doradus
11.12.2005
In the center of star-forming region 30 Doradus lies a huge cluster of the largest, hottest, most massive stars known. These stars, known as the star cluster R136, and part of the surrounding nebula are captured here in this gorgeous visible-light image from the Hubble Space Telescope.
 Hubble s Cosmic Reef
Hubble s Cosmic Reef
25.04.2020
These bright ridges of interstellar gas and dust are bathed in energetic starlight. With its sea of young stars, the massive star-forming region NGC 2014 has been dubbed the Cosmic Reef. Drifting just...
 Globular Cluster 47 Tucanae from SALT
Globular Cluster 47 Tucanae from SALT
5.09.2005
Stars come in bunches. Of the over 200 globular star clusters that orbit the center of our Milky Way Galaxy, 47 Tucanae is the second brightest globular cluster, behind Omega Centauri. Known to some affectionately as 47 Tuc or NGC 104, it is only visible from Earth's Southern Hemisphere.
 Globular Star Cluster 47 Tuc
Globular Star Cluster 47 Tuc
10.03.2022
Globular star cluster 47 Tucanae is a jewel of the southern sky. Also known as NGC 104, it roams the halo of our Milky Way Galaxy along with some 200 other globular star clusters. The second brightest globular cluster (after Omega Centauri) as seen from planet Earth, 47 Tuc lies about 13,000 light-years away.
 Galaxies from the Altiplano
Galaxies from the Altiplano
13.10.2016
The central bulge of our Milky Way Galaxy rises over the northern Chilean Atacama altiplano in this postcard from planet Earth. At an altitude of 4500 meters, the strange beauty of the desolate landscape could almost belong to another world though.
 Sweeping Through Southern Skies
Sweeping Through Southern Skies
16.02.2013
For now, Comet Lemmon (C/2012 F6a), and Comet PanSTARRS (C/2011 L4) are sweeping through southern skies. Lemmon's lime green coma and thin tail are near the left edge of this telephoto scene, a single frame from a timelapse video (vimeo here) recorded on February 12, tracking its motion against the background stars.
 NGC 6822: Barnard s Galaxy
NGC 6822: Barnard s Galaxy
2.12.2021
Grand spiral galaxies often seem to get all the glory, flaunting their young, bright, blue star clusters in beautiful, symmetric spiral arms. But small galaxies form stars too, like nearby NGC 6822, also known as Barnard's Galaxy.
 The Mysterious Rings of Supernova 1987A
The Mysterious Rings of Supernova 1987A
26.02.2012
What's causing those odd rings in supernova 1987A? Twenty five years ago, in 1987, the brightest supernova in recent history was seen in the Large Magellanic Clouds. At the center of the above picture is an object central to the remains of the violent stellar explosion.
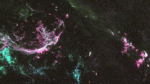 Supernova Remnant: Cooking Elements In The LMC
Supernova Remnant: Cooking Elements In The LMC
9.05.1996
Massive stars cook elements in their cores through nuclear fusion. Starting with the light elements of hydrogen and helium, their central temperatures and pressures produce progressively heavier elements, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, etc. up through iron.
|
January February March |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||