
|
You entered: massive stars
 Galaxy Cluster in the Early Universe
Galaxy Cluster in the Early Universe
26.02.2004
Long before medieval alchemists dreamed of transmuting base metals to gold, stellar furnaces in this massive cluster of galaxies - cataloged as RDCS 1252.9-2927 - had transformed light elements into heavy ones. In the false-color composite image individual cluster galaxies can be seen at optical and near-infrared wavelengths, shown in red, yellow, and green colors.
 Runaway Star Alpha Camelopardalis
Runaway Star Alpha Camelopardalis
28.04.2023
Like a ship plowing through cosmic seas, runaway star Alpha Camelopardalis has produced this graceful arcing bow wave or bow shock. The massive supergiant star moves at over 60 kilometers per second through space, compressing the interstellar material in its path.
 Mountains of Creation
Mountains of Creation
11.11.2005
This fantastic skyscape lies at the eastern edge of giant stellar nursery W5, about 7,000 light-years away in the constellation Cassiopeia. An infrared view from the Spitzer Space Telescope, it features interstellar clouds...
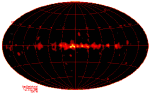 COMPTEL Explores The Radioactive Sky
COMPTEL Explores The Radioactive Sky
24.07.1996
Diffuse gas clouds laced with radioactive aluminum atoms (Al26) line the plane of our Milky Way Galaxy! How do we see them? Relying on the Compton Effect, the COMPTEL instrument onboard NASA's immense orbiting Compton Gamma Ray Observatory can "see" the 1.8 million electron Volt gamma rays emitted by the radioactive decay.
 Mountains of Creation
Mountains of Creation
15.12.2007
(xxxedit and linkxxx) This fantastic skyscape lies at the eastern edge of giant stellar nursery W5, about 7,000 light-years away in the constellation Cassiopeia. An infrared view from the Spitzer Space Telescope...
 The Great Carina Nebula
The Great Carina Nebula
27.10.2007
A jewel of the southern sky, the Great Carina Nebula, aka NGC 3372, spans over 300 light-years, one of our galaxy's largest star forming regions. Like the smaller, more northerly Orion Nebula...
 The Great Carina Nebula
The Great Carina Nebula
19.04.2024
A jewel of the southern sky, the Great Carina Nebula is more modestly known as NGC 3372. One of our Galaxy's largest star forming regions, it spans over 300 light-years. Like the smaller, more northerly Great Orion Nebula, the Carina Nebula is easily visible to the unaided eye.
 Small Star
Small Star
5.06.1997
A dim double star system cataloged as Gliese 623 lies 25 light-years from Earth, in the constellation of Hercules. The individual stars of this binary system were distinguished for the first time when the Hubble Space Telescope's Faint Object Camera recorded this image in June 1994.
 Cataclysmic Dawn
Cataclysmic Dawn
10.01.2015
Will this dawn bring another nova? Such dilemmas might be pondered one day by future humans living on a planet orbiting a cataclysmic variable binary star system. Cataclysmic variables involve gas falling from a large star onto an accretion disk surrounding a massive but compact white dwarf star.
 Stars, Gas, and Dust Battle in the Carina Nebula
Stars, Gas, and Dust Battle in the Carina Nebula
15.08.2017
Chaos reigns in the Carina Nebula where massive stars form and die. Striking and detailed, this close-up of a portion of the famous nebula is a combination of light emitted by hydrogen (shown in red) and oxygen (shown in blue).
|
January February |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||