
|
You entered: ASCA
 ASCA X-Ray Observatory
ASCA X-Ray Observatory
20.02.1996
Today marks the third anniversary of the launch of the Advanced Satellite for Cosmology and Astrophysics (ASCA; renamed from Astro D when launched). ASCA, seen here superposed on galaxy M31, is a Japanese satellite for which NASA has provided some scientific equipment. ASCA carries four large-area X-ray telescopes.
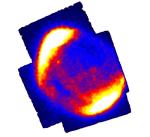 SN 1006: Pieces of the Cosmic Ray Puzzle
SN 1006: Pieces of the Cosmic Ray Puzzle
2.12.2000
Research balloon flights conducted in 1912 by Austrian physicist Victor Hess revealed that the Earth was constantly bombarded by high energy radiation from space - which came to be called "Cosmic Rays". What are Cosmic Rays and where do they come from?
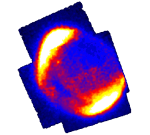 SN 1006: Pieces of the Cosmic Ray Puzzle
SN 1006: Pieces of the Cosmic Ray Puzzle
16.10.1996
Research balloon flights conducted in 1912 by Austrian physicist Victor Hess revealed that the Earth was constantly bombarded by high energy radiation from space - which came to be called "Cosmic Rays". What are Cosmic Rays and where do they come from?
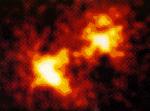 An X-ray Hot Supernova in M81
An X-ray Hot Supernova in M81
3.12.1995
In 1993, a star in the galaxy M81 exploded. Above is a picture of the hot material ejected by this supernova explosion. The picture was taken in X-rays with the Advanced Satellite for Cosmology and Astrophysics (ASCA).
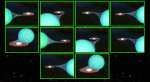 Black Hole Signature From Advective Disks
Black Hole Signature From Advective Disks
15.01.1997
What does a black hole look like? If alone, a black hole would indeed appear quite black, but many black hole candidates are part of binary star systems. So how does a black hole binary system look different from a neutron star binary system? The above drawings indicate it is difficult to tell!
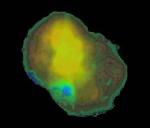 X-Rays From IC 443
X-Rays From IC 443
2.05.1997
The life-cycles of stars help drive the ecology of our Galaxy, churning, processing, and redistributing matter. Massive stars reach a spectacular evolutionary endpoint - supernovae explosions which blast off their outer layers, violently merging stellar material with the gas and dust of the Milky Way. The supernova remnant IC 443 is typical of the aftermath.
 Hubble Floats Free
Hubble Floats Free
6.03.1997
Why put observatories in space? Most telescopes are on the ground. On the ground, you can deploy a heavier telescope and upgrade it more easily. The trouble is that Earth-bound telescopes must look through the Earth's atmosphere.
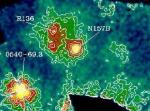 Ultra Fast Pulsar
Ultra Fast Pulsar
11.02.1998
Pulsars are rotating neutron stars, born in the violent crucibles of supernova explosions. Like cosmic lighthouses, beams of radiation from surface hotspots sweep past our viewpoint creating pulses which reveal the rotation rates of these incredibly dense stellar corpses. The most famous pulsar of all is found in the nearby supernova remnant, the Crab Nebula.
|
January February |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||