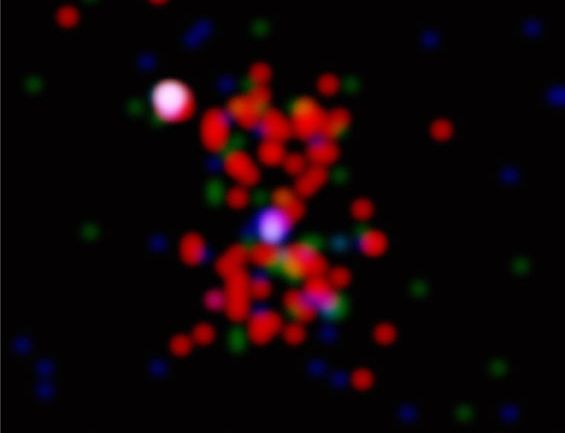
Credit: A. Fabian
(IoA Cambridge) et al.,
NASA
Explanation:
Large
clusters of galaxies
are the most massive objects in the universe.
Astronomers now realize that a hallmark of these cosmic behemoths
are gas clouds with temperatures of tens of millions of
degrees that
pervade the clusters and radiate
strongly in x-rays.
This
Chandra Observatory image
centered on a
radio galaxy cataloged as
3C294 indeed reveals the telltale
hot x-ray gas in an hourglass shaped
region surrounding the dominant galaxy and
shows the presence of a massive galaxy cluster in the
distant universe.
Here the picture is color-coded by x-ray energy, red for low, green
for medium, and blue for high energy x-rays.
The cluster associated with 3C294
is 10 billion light-years away making it the
most distant x-ray galaxy cluster
ever detected.
Objects at that extreme distance existed when the universe was
young, a mere 20 percent of its present age.
Impressively, this observation demonstrates that even at those early
times massive
clusters of galaxies were already present.
1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 |
Январь Февраль Март Апрель Май Июнь Июль Август Сентябрь Октябрь Ноябрь Декабрь |
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
|
Публикации с ключевыми словами:
cluster of galaxies - intracluster gas - 3c294 - X-ray - рентгеновское излучение - межгалактический газ - Скопление галактик
Публикации со словами: cluster of galaxies - intracluster gas - 3c294 - X-ray - рентгеновское излучение - межгалактический газ - Скопление галактик | |
См. также:
Все публикации на ту же тему >> | |