|
Credit & Copyright: X-ray - NASA/CXC/Rutgers/G.Cassam-Chenai, J.Hughes et al.;
Radio - NRAO/AUI/NSF/GBT/VLA/
Dyer, Maddalena & Cornwell; Optical - Middlebury College/F.Winkler, NOAO/AURA/NSF/CTIO Schmidt & DSS
Explanation:
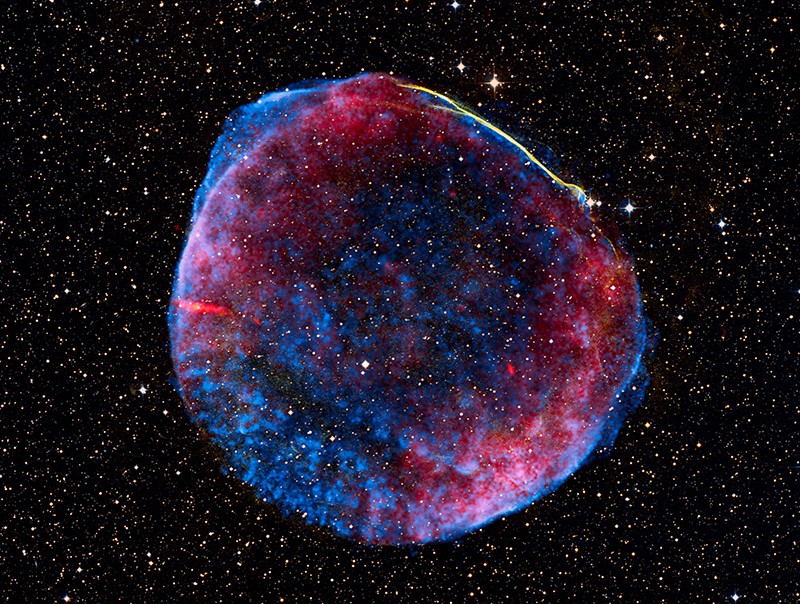
A new star, likely the brightest supernova
in recorded human
history, lit up
planet Earth's sky in the year 1006 AD.
The expanding debris cloud from the stellar explosion,
found in the southerly constellation
of Lupus,
still puts on a cosmic light show across the
electromagnetic spectrum.
In fact, this
composite view includes
X-ray data in blue from the
Chandra Observatory,
optical data in
yellowish hues, and radio image data in red.
Now known as the SN 1006
supernova remnant, the debris cloud
appears to be about 60 light-years across and is understood
to represent the remains of a white dwarf star.
Part of a binary star system,
the compact white dwarf gradually
captured material from its companion star.
The buildup in mass finally triggered a
thermonuclear
explosion that destroyed the dwarf star.
Because the distance to the supernova remnant is about 7,000
light-years, that explosion actually
happened 7,000 years before the light reached Earth in 1006.
Shockwaves in the remnant
accelerate
particles to extreme energies and are
thought to be a source of the mysterious
cosmic rays.
Dyer, Maddalena & Cornwell; Optical - Middlebury College/F.Winkler, NOAO/AURA/NSF/CTIO Schmidt & DSS
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Based on Astronomy Picture
Of the Day
Publications with keywords: supernova - SN type Ia - white dwarf - supernova remnant - cosmic rays
Publications with words: supernova - SN type Ia - white dwarf - supernova remnant - cosmic rays
See also:
- Planetary Nebula Abell 7
- APOD: 2026 January 19 Á CTB 1: The Medulla Nebula
- APOD: 2026 January 7 Á Simeis 147: The Spaghetti Nebula Supernova Remnant
- APOD: 2025 December 29 Á M1: The Crab Nebula
- APOD: 2025 November 5 Á Spiral Galaxy NGC 3370 from Hubble
- APOD: 2025 October 1 Á NGC 6960: The Witchs Broom Nebula
- APOD: 2025 July 31 Á Supernova 2025rbs in NGC 7331