
|
You entered: Observatory
 Under the Galaxy
Under the Galaxy
13.10.2017
The Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, stands above the southern horizon in this telephoto view from Las Campanas Observatory, planet Earth. In the dark September skies of the Chilean Atacama desert, the small galaxy has an impressive span of about 10 degrees or 20 Full Moons.
 The Milky Way Over Paranal
The Milky Way Over Paranal
23.01.2007
It's not the sky that's falling. More accurately, the Earth is rising. The Earth's rotation gives a continually changing view to all Earth observers, including those measuring the universe at the Paranal Observatory.
 Mars Moons
Mars Moons
24.10.2003
This year's record close approach of Mars inspired many to enjoy telescopic views of the red planet. But while Mars was so bright it was hard to miss, spotting Mars' two diminutive moons was still a good test for observers with modest sized instruments.
 The Arms of NGC 7424
The Arms of NGC 7424
16.12.2004
The grand, winding arms are almost mesmerizing in this face-on view of NGC 7424, a spiral galaxy with a prominent central bar. About 40 million light-years distant in the headlong constellation Grus, this island universe is also about 100,000 light-years across making it remarkably similar to our own Milky Way.
 M74: The Perfect Spiral
M74: The Perfect Spiral
4.10.2001
If not perfect, then this spiral galaxy is at least one of the most photogenic. An island universe of about 100 billion stars, 30 million light-years away toward the constellation Pisces, NGC 628 or M74 presents a gorgeous face-on view to earthbound astronomers.
 Henrietta Leavitt Calibrates the Stars
Henrietta Leavitt Calibrates the Stars
3.09.2000
Humanity's understanding of the relative brightness and variability of stars was revolutionized by the work of Henrietta Swan Leavitt (1868-1921). Working at Harvard College Observatory, Leavitt precisely calibrated the photographic magnitudes of 47 stars to which all other stars could be compared.
29.10.1995
When massive stars explode they create large radioactive blast clouds which expand into interstellar space. As the radioactive elements decay, they produce gamma-rays. Possible locations of these stellar explosions known as supernovae, are indicated by the bright clumps in this map of the central regions of our Milky Way Galaxy.
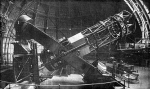 The Hooker Telescope on Mt. Wilson
The Hooker Telescope on Mt. Wilson
1.07.1995
In the 1920s, pictures from the Hooker Telescope on Mt. Wilson fundamentally changed our understanding of the cosmos. Astronomer Edwin Hubble, using photographs he took with this telescope, demonstrated that the objects his contemporaries called "spiral nebulae" were actually huge systems of stars - spiral galaxies, similar to our own Milky Way galaxy but incredibly distant.
 Galaxies in the GOODS
Galaxies in the GOODS
25.06.2003
This tantalizing view of galaxies scattered near and far is part of the Hubble Space Telescope's contribution to the GOODS - the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey project. The GOODS' goal is to study...
 Halo and Hexagons
Halo and Hexagons
9.11.2006
As a bright November Moon lit up the night sky last week, Gil Esquerdo spotted this lovely Moon halo overhead at the Whipple Observatory on Mt. Hopkins, Arizona. In the foreground, the structure...
|
January February |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||