
|
You entered: hydrogen
 Uranus: The Tilted Planet
Uranus: The Tilted Planet
15.11.1997
Uranus is the third largest planet after Jupiter and Saturn. This picture was snapped by the Voyager 2 spacecraft in 1986 - the only spacecraft ever to visit Uranus. Uranus has many moons and a ring system. Uranus is composed mostly of rock and ices, but with a thick hydrogen and helium atmosphere.
 Jupiter from Voyager
Jupiter from Voyager
18.07.1999
This picture of the planet Jupiter was taken by the Voyager 1 spacecraft as it passed the planet in 1979. Jupiter, a gas giant planet with no solid surface, is the largest planet in the Solar System and is made mostly of the hydrogen and helium.
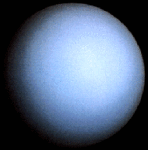 Uranus: The Tilted Planet
Uranus: The Tilted Planet
16.08.1995
This picture was snapped by the Voyager 2 spacecraft in 1986 - the only spacecraft ever to visit Uranus. Uranus is the third largest planet after Jupiter and Saturn. Uranus has many moons and a ring system.
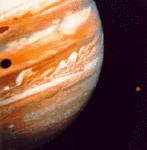 Jupiter, Io, and Ganymede's Shadow
Jupiter, Io, and Ganymede's Shadow
13.10.1995
Jupiter, the solar system's largest planet, is seen here next to Io, its closest Galilean moon. On the cloud tops of Jupiter near the left edge of the picture can be seen a dark circular spot which is caused by the shadow of Jupiter's largest moon Ganymede.
 Eagle EGGs in M16
Eagle EGGs in M16
12.08.2001
Star forming regions known as "EGGs" are uncovered at the end of this giant pillar of gas and dust in the Eagle Nebula (M16). EGGs, short for evaporating gaseous globules, are dense regions of mostly molecular hydrogen gas that fragment and gravitationally collapse to form stars.
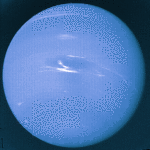 Neptune: Big Blue Giant
Neptune: Big Blue Giant
21.02.1998
This picture was taken by the Voyager 2 spacecraft in 1989 - the only spacecraft ever to visit Neptune. Neptune will be the farthest planet from the Sun until 1999, when the elliptical orbit of Pluto will cause it to once again resume this status.
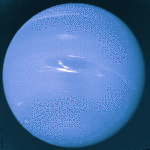 Neptune: Big Blue Giant
Neptune: Big Blue Giant
17.08.1995
This picture was taken by the Voyager 2 spacecraft in 1986 - the only spacecraft ever to visit Neptune. Neptune will be the farthest planet from the Sun until 1999, when the elliptical orbit of Pluto will cause it to once again resume this status.
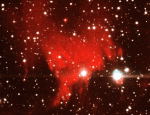 Nebula Nova Cygni Turns On
Nebula Nova Cygni Turns On
16.12.1996
Old photographs show no evidence of the above nebula. In 1992, a white dwarf star in Cygnus blew off its outer layers in a classical nova explosion: an event called Nova Cygni 1992. Light flooded the local interstellar neighborhood, illuminated this existing gas cloud, excited the existing hydrogen, and hence caused the red emission.
 M8: The Lagoon Nebula
M8: The Lagoon Nebula
7.07.1998
The bright Lagoon Nebula is home to a diverse array of astronomical objects. Particularly interesting sources include a bright open cluster of stars and several energetic star-forming regions. The general red glow is caused by luminous hydrogen gas, while the dark filaments are caused by absorption by dense lanes of dust.
 Eagle Eggs in M16
Eagle Eggs in M16
28.02.1998
Star forming regions known as "EGGs" are uncovered at the end of this giant pillar of gas and dust in the Eagle Nebula (M16). EGGs, short for evaporating gaseous globules, are dense regions of mostly molecular hydrogen gas that fragment and gravitationally collapse to form stars.
|
January February |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||