
|
You entered: supernova
 M1: Polarization of the Crab
M1: Polarization of the Crab
23.11.1995
The Crab Nebula resulted from a star that exploded - a supernova. Although the stellar explosion that caused the Crab Nebula was seen over 900 years ago, the nebula itself still expands and shines. Much of the emitted light has been found to be polarized. Light waves with the same polarization vibrate in the same plane.
 Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse
19.04.1998
Here is the first direct picture of the surface of a star other than our Sun. Taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in 1995, the atmosphere of Betelgeuse reveals some unexpected features, including a large bright hotspot visible below the center.
 In the Center of the Keyhole Nebula
In the Center of the Keyhole Nebula
21.07.1997
Stars, like people, do not always go gentle into that good night. The above Keyhole Nebula results from dying star Eta Carinae's violently casting off dust and gas during its final centuries. Eta Carinae is many times more massive than our own Sun, and should eventually undergo a tremendous supernova explosion.
 On the Origin of Gold
On the Origin of Gold
15.10.2017
Where did the gold in your jewelry originate? No one is completely sure. The relative average abundance in our Solar System appears higher than can be made in the early universe, in stars, and even in typical supernova explosions.
 M83: The Southern Pinwheel Galaxy from VLT
M83: The Southern Pinwheel Galaxy from VLT
11.05.2003
M83 is one of the closest and brightest spiral galaxies on the sky. Visible with binoculars in the constellation of Hydra, majestic spiral arms have prompted its nickname as the Southern Pinwheel. Although discovered...
 In the Center of NGC 604
In the Center of NGC 604
5.03.1997
Stars are sometimes born in the midst of chaos. About 3 million years ago in the nearby galaxy M33, a large cloud of gas spawned dense internal knots which gravitationally collapsed to form stars. But NGC 604 was so large, it could form enough stars to make a globular cluster.
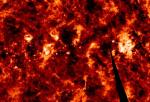 The Frothy Milky Way
The Frothy Milky Way
2.05.1998
Astronomers have discovered that looking at dust along the plane of our Milky Way Galaxy is a bit like looking into a frothy glass of beer. The dust between stars in our galaxy appears...
 Henize 70: A Superbubble in the LMC
Henize 70: A Superbubble in the LMC
4.02.2019
Massive stars profoundly affect their galactic environments. Churning and mixing interstellar clouds of gas and dust, stars -- most notably those upwards of tens of times the mass of our Sun -- leave their mark on the compositions and locations of future generations of stars.
 What the Hubble Saw
What the Hubble Saw
25.11.2004
In this striking 41 inch by 38 inch quilt, astronomy enthusiast Judy Ross has interpreted some of the Hubble Space Telescope's best galactic and extragalactic vistas. Featured in past APODs, clockwise from...
 Henize 70: A SuperBubble In The LMC
Henize 70: A SuperBubble In The LMC
13.06.1998
Stars with tens of times the mass of the Sun profoundly affect their galactic environment. Churning and mixing the interstellar gas and dust clouds they leave their mark in the compositions and locations of future generations of stars and star systems.
|
January February |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||